Abstract The paper discusses the characteristics of waste papermaking wastewater and analyzes and evaluates the waste paper papermaking wastewater treatment technology. It is pointed out that using coagulation sedimentation-biochemical method or chemical treatment-coagulation sedimentation method can effectively control waste papermaking wastewater.
Key words waste papermaking wastewater, characteristics of wastewater, coagulation and sedimentation, biochemical method, chemical method
Because waste paper recycling paper can effectively use resources and protect the ecological environment, it has received increasing attention from people. With the continuous maturation of waste paper pulping technology, waste paper has become an important raw material for the production of pulp. In 1995, foreign waste paper accounted for 30% to 34% of raw materials for pulp production [1]. In recent years, China's waste paper recycling papermaking plants are also increasing.
In order to separate the fibers from the waste paper and remove the ink from the fibers, a large amount of chemicals are often added during the production process, and various impurities in the waste paper are removed by washing. Therefore, waste paper recycling and papermaking will produce a large amount of wastewater containing fine fiber inks, resins, pigments, chemicals, and mechanical impurities.
Compared with the process of direct utilization of plant fiber pulping, the pollution load of waste paper recycled papermaking wastewater is relatively light, but it still far exceeds the emission standards. If it is discharged without treatment, it will cause environmental pollution and harm [2] ]. With the continuous increase in the proportion of waste paper recycling, waste paper papermaking wastewater has attracted people's attention. In recent years, a series of treatment technologies have been developed for the characteristics of waste paper papermaking wastewater, laying the foundation for the effective treatment of such wastewater.
1 Waste papermaking wastewater characteristics
The waste paper recycling and papermaking process can be divided into pulping and papermaking. In the process of de-slurry, washing and rinsing of the pulping part, a large amount of washing waste water is generated. According to the difference of the waste paper source and the production process, the characteristics of the washing wastewater are different. The pollutant content is approximately: CODCr 600-2400 mg/L, BOD5 125-585 mg/L, SS 650-2400 mg/L, color Degree of 450 to 900 times, the appearance of dark gray. The amount of washing waste water is 100 to 200 t/ton of paper [3 to 5]. Like the ordinary papermaking process, “white water†containing fibers, fillers, and chemicals is also produced in the papermaking part of waste paper recycled papermaking. The waste water is often treated by air floatation to recover the fibers and fillers, and the treated “white water†can be recycled. In China, the "white water" treatment technology has matured.
It can be seen that the waste paper used for recycling paper and paper is mainly derived from the pulp washing waste water. The waste water not only has a high SS content and a large chroma, but also contains a large amount of COD substances having a complicated composition. These COD substances consist of organic substances such as soluble slurries, chemical additives, and insoluble fibers. In the soluble COD component, it basically consists of a low molecular weight component with a molecular weight of less than 1000 (such as soluble matter in waste paper pulp) and a high molecular weight component with a molecular weight of 100,000 or more (such as chemicals, resins, etc.). The molecular weight of the middle component is very small [6].
Since the molecular weight of COD components in waste papermaking wastewater is quite different, only a part of COD substances can be removed by a single treatment method, and it is difficult to obtain satisfactory results. Therefore, comprehensive treatment technology must be adopted.
The coagulation and sedimentation method can remove the COD components with higher molecular weight in the wastewater, while the biochemical and adsorption methods can remove COD components with lower molecular weight.
The waste paper papermaking wastewater treatment technology developed earlier in China is a coagulation and sedimentation method. With the application of new organic and inorganic polymer flocculants, the coagulation and sedimentation method can not only effectively remove the SS and color in the wastewater, but also greatly reduce the COD content of the wastewater. This method has been applied in some factories. Since coagulation and sedimentation cannot remove COD components with lower molecular weight, it is difficult to achieve effective treatment of wastewater. In recent years, researchers have studied the advanced treatment of waste paper papermaking wastewater, and successively developed techniques such as coagulation-sedimentation-biochemical method, chemical treatment-coagulation and sedimentation method. The following describes these processing technologies.
2 Waste papermaking wastewater treatment methods
2.1 Coagulation and sedimentation
The coagulation and sedimentation method has the characteristics of simple process, convenient operation, high efficiency and low investment. The basic principle is as follows: Under the action of coagulant, the electrochemical process of compressing the surface of the micro-particles, reducing the potential of the interface, electrochemical neutralization, and other physical and chemical processes such as bridging, trapping, and adsorption will be used to treat the wastewater. The suspended solids, colloids and other flocculateable substances condense into a "flocculation"; the flocculated waste water is then subjected to solid-liquid separation by a settling device, and the "floc" sinks into the bottom of the settling device and becomes a slurry, which flows out of the top. It is clean water with low chroma and turbidity.
Practice has proved that using the coagulation and sedimentation method to treat waste papermaking wastewater, the SS removal rate can reach 85% to 98%, the color removal rate can reach more than 90%, CODCr removal rate can reach 60% to 80%. Since the treated clean water is of good quality, it can be reused for washing and papermaking; the resulting slurry can be reused as linerboard pulp [7]. The process flow of waste paper papermaking wastewater treatment by the coagulation and sedimentation method is shown in Figure 1.
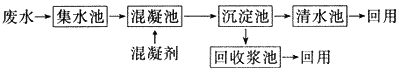
Fig.1 Process flow of waste paper papermaking wastewater treatment by coagulation and sedimentation
The effect of coagulation and sedimentation on waste papermaking wastewater treatment depends on the quality of the coagulation process. First, the appropriate coagulant should be selected. At present, inorganic and organic polymer coagulants are mainly used, such as polyferric sulfate, polyaluminum chloride, complexes of binary or ternary metal salts, polyacrylamides and their derivatives. One or two of the visible waste water conditions are used. The author's research shows that the inorganic and organic polymer coagulants can effectively improve the flocculating quality of wastewater, and the obtained “Jinhua†is large and dense with good treatment effect. Other factors that affect the coagulation process, such as the amount of coagulant added, the way the coagulant is added, the coagulation reaction time, etc. can be determined experimentally.
If the treated waste pulp and fresh water can be reused, the coagulation and sedimentation method also has better economic benefits. Under normal operating conditions, the cost of treatment of 1 t waste water for coagulant is 0.1-0.2 yuan, and the total treatment cost should be around 0.5 yuan. However, due to the benefits of reuse of water and pulp, as well as reductions in expenditures such as sewage charges and resource use fees, there are significant economic benefits.
Because the coagulation and sedimentation method can only remove part of the COD material, it is difficult to meet the emission requirements for the COD content of the treated wastewater. This is the reason that the coagulation and sedimentation method has great limitations in practical applications. (to be continued)