Once the sample is cleaned, it is transferred to an external Dewar (or other thermostatic bath) to maintain it at a constant temperature. Then, a small amount of gas (adsorbed material, that is, adsorbate) is gradually introduced into the sample tube that is evacuated. The adsorbate molecules entering the sample tube quickly reach the surface of each well on the solid sample (ie, the adsorbent). If the sample has both micropores and mesopores, then the adsorption isotherm should contain the following stages:
1)
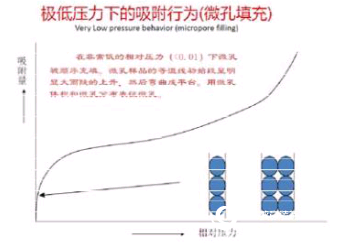
Micropore filling at very low pressure (relative pressure less than 0.01) Zone: The initial section of the isotherm containing the microwell sample showed a significant large and steep rise and then was bent into a platform. The data from this curve can characterize the micropore volume and micropore distribution. Since the pore size is close to the diameter of the gas molecule, it is necessary to select the correct adsorbate gas. ?
2)
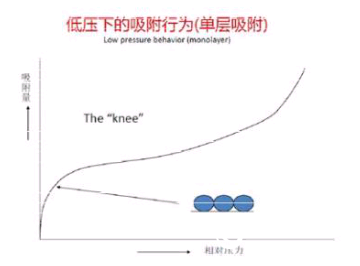
Single-layer adsorption zone: As more and more gas molecules are introduced into the system, when the micropores are filled, the adsorbate molecules form a thin layer across the surface of the adsorbent. The adsorption isotherm exhibits a knee-like curvature. ?
3)
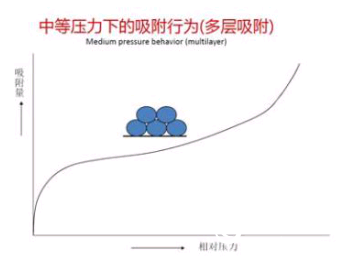
Multi-layer adsorption zone: Immediately following the adsorption curve into the platform zone, it was shown that surface multi-layer adsorption occurred here. The BET theory requires exactly the specific surface area of ​​the adsorption curve data at this stage. ?
4)
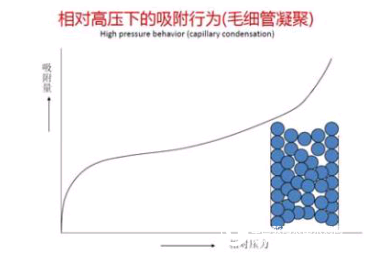
Capillary Condensation Zone: When the relative pressure is greater than 0.4, continuous multi-layer adsorption is accompanied by a capillary condensation process. Capillary condensation is the process in which the adsorbed gas in the channel is converted into a liquid with increasing partial pressure ratio. The classical equation describing this process is the Kelvin equation. This equation quantifies the ratio of the equilibrium gas pressure to the capillary size at which the gas can be condensed. Using the Barrett,? Joyner? And? Halenda? (BJH)? Calculation method may be calculated according to the equilibrium pressure of the gas aperture, resulting cumulative or differential pore size distribution. ??
As the equilibrium pressure of the adsorbate tends to be saturated, the pores of the adsorbent will be completely filled by the adsorbate. If you know the density of the adsorbate, you can calculate the volume it takes, and then calculate the total pore volume of the sample accordingly. If we reverse the adsorption process at this time and gradually reduce the amount of gas from the system, we can get the desorption isotherm. Due to the different mechanisms of adsorption and desorption, adsorption and desorption isotherms rarely overlap. The hysteresis of the isotherm is related to the pore shape of the solid particles. ?
Aluminium Foil Container,Foil Container,Unlined Alu Foil Container,Oven Aluminium Foil Container
NINGBO FAVORED COMMODITY CO.,LTD , https://www.favored-top.com